Articles
Recent Articles
pH Testing in Wastewater Treatment
The pH of the environment has a profound effect on the rate of microbial growth. pH affects the function of metabolic enzymes. Acidic conditions (low pH) or basic conditions (high pH) alter the structure of the enzyme and stop growth. Most microorganisms do well...

Chemical Oxygen Demand Testing
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) relies on chemical oxidation with chromic acid (a strong oxidizer). Many organic compounds, including color bodies and fibers, which are not easily biodegradable, along with any inorganic chemicals will show up as chemical oxygen demand...

Dissolved Oxygen Uptake Rate (DOUR) Test
Biological waste treatment in the Aerated Stabilization Basin (ASB) process and in Activated Sludge systems is based on the ability of microorganisms to utilize dissolved oxygen in the process of breaking down the soluble organic substances present in the process...

Troubleshooting Aerated Stabilization Basin
Aerated Stabilization Basin (ASBs) performance can be associated with numerous root causes, both chronic and intermittent. The three main conditions leading to loss of system performance and potential permit violations are discussed below. Temporary upsets due to...
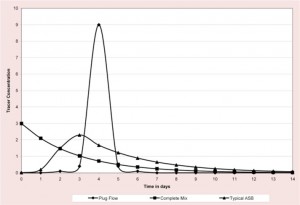
Eight Growth Pressures of Biological Treatment in Aerated Stabilization Basins: Part 5
Part 5 of 8: Retention Time and Flow Patterns Time is the bacteria's friend. Long retention times reduce the system's dependence on bacterial reproduction and reduce nutrient requirements. Retention time is also critical so that log growth can be completed and...
Eight Growth Pressures of Biological Treatment in Aerated Stabilization Basins: Part 4
Part 4 of 8: Dissolved Oxygen Dissolved oxygen is a critical growth pressure. The presence or absence of dissolved oxygen determines the type of metabolism. Much has been written and discussed the proper dissolved oxygen residual...
Featured Articles
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
